Selective credit control in Netherland 1955 - Lesson learned from Grebler (1955) paper
Posted by: admin 1 year, 9 months ago
(Comments)
In 1955
In early 1955, maladjustments following in the wake of the rapid expansion in home building became more and more evident. In January it was reported that rental vacancies were increasing as tenants were drawn into purchases of homes with little or no cash requirements. Indications of rising vaèancies continued, and by spring there was substantial public discussion of "overbuilding." 1 Special surveys by local FHA and V.A. offices, which were initiated at that time, showed actual or emerging surpluses of newhomes offered for sale in an increasing number of cities. As ,for rental housing, the average vacancy rate in FHA-financed projects at the end of March 1955 stood at 4.4 per cent as against 3.5 per cent the year before and 2.8 per cent in 1953. More significantly, 38 of the 75 field offices reported vacancy rates in excess of 5 per cent compared with only 24 the year before, and 12 offices showed vacancies of i o per cent or more. Among the latter were field districts which included large cities such as Providence, Indianapolis, Little Rock, New Orleans, Oklahoma City, Fort Worth, Houston, and San Diego.2 Despite the inadequacy of data on the current state of the housing market and the difficulty of interpreting widely varying local conditions, it became obvious that the sale of the unusually large number of homes that had been started in the latter part of 1954 and early 1955 was difficult in many areas. Particularly in the West and the South where housing starts hadincreased most, builders offered cash payments for moving expenses andpremiums of one kind or another in order to promote sales; one of theinducements was the "no-no down-payment" Joan already referred to inthe preceding chapter. These marketing practices, together with increasingvacancies, clearly indicated that the rate of housing starts in late 1954 andearly 1955 to 1.4 million units) could not be sustained for long at current prices for homes even on the very generous financing terms thenavailable to home builders and purchasers. Further maladjustments appeared in the form of shortages of a varietyof building materials and of price rises. While the rate of housing starts leveled off after December 1954, expenditures for new residential construction, which are the more pertinent measure of pressures on resources, kept on increasing sharply throughout the first half of 1955. Already in Januarysupply difficulties were reported for gypsum, composition sheeting, andplasterboard.3 Later, cement, copper and brass products, and structural steel
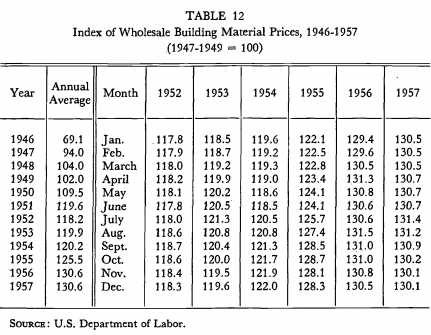
joined the in short supply, and construction delays became more frequent. Wholesale prices of building materials had begun to move up inthe second half of i and they increased—2.g per cent between July 1954and April 1955 (Table 12)—at a faster rate than prices of industrial cornmodities as a whole. While construction costs rose only moderately (Table 7), the price of land apparently rose more sharply.4 Thus, inflationary pressures in residential construction were apparent before the general advance of industrial prices in the summer of 1955. Although the financial markets had become slightly firmer in the second half of i and residential mortgage commitments had ceased to expand late that year, mortgage recordings and the home mortgage debt increasedsharply and much of this increase occurred in the government-underwrittensector of the market, particularly under the veterans' home loan program. Reflecting earlier commitment and financing arrangements, credit terms onloans closed during the first few months of the year were progressively moreliberal, as is evident from the further increase in no-down-payment andlong-maturity loans to veterans (Chart 3 and Table 26). As lenders wereunable to absorb the rapidly growing volume of mortgage loans and meet the rising demand for other long-term funds, they resorted increasingly tothe use of short-term credit to help them fulfill the heavy commitments made earlier. This condition was dramatized in January 1955 when the press reported that the Prudential Insurance Company had made a "mortgagewarehousing" agreement with a syndicate of i 50 commercial banks in theamount of $350 million.5 This was the first time an insurance company hadbeen known to enter into a mortgage warehousing arrangement directly. It was also the largest single mortgage warehousing transaction ever reported, and the terms of• 12 to i8 months were longer than usual. These developments in the housing and mortgage markets coincided withthe accelerated pace of general economic recovery. By late i the recoveryhad made up but half the previous decline in industrial output. Outlays onplant and equipment and federal spending were still moving downward. The liquidation of inventories had just come to a halt. In the spring of 1955, however, expenditures for plant and equipment began to increase, and thedecline in federal spending ceased. Private nonresidential construction was expanding, although less than the residential sector. Largely reflecting thebooming automobile market, consumer purchases rose more rapidly. Stockprices continued to climb, and both commercial bank loans and consumer credit increased sharply. Thus, there was a swift convergence of expansionary forces: The Federal Reserve authorities responded to the evolving business expansion with caution. The policy of "active credit ease" was changed to one of "ease" in December 1954. In January, the directive for open-market operations modified this policy further without, however, calling for a program of restraint, and stock margin requirements were raised. In April, discount rates were increased moderately from 1.5 to i per cent, and stock marginrequirements were raised again. In May, the objective to "encourage recovcry" was deleted from the directive for open-market operations. Throughout the second quarter of the year, these operations had little net effect on bank reserves. A clear policy of restraint was not initiated before early August.6 It was under these conditions that selective controls on housing credit were considered and put into effect.
Source : https://www.nber.org/system/files/chapters/c2411/c2411.pdf
3 weeks ago
What does the Fed do in 2008
Recent newsToday, one of the popular topic related to financial policy is the question on
read more3 weeks ago
What is Lifetime Value of customer
Recent newsHave you ever heard about LTV? well if you talk about Macroprudential policy, it will be loan to value. But if you talk about startups and the world of tech, it refers to the Lifetime value of a company.
read more1 month, 2 weeks ago
Mengenal lebih dalam kurikulum merdeka
Recent newsAkhirnya Indonesia menerapkan kurikulum merdeka, namun sebenarnya apa sih itu kurikulum merdeka?
read more1 month, 3 weeks ago
How to understand the impact of interactive variable from interaction model to depended variable
Recent newsI tried from my own research. And here it is
read more2 months ago
Thing you should do, to not clutter the social media
Recent newsThere 7 things that really move the needle when it comes to social media. They aren’t always easy, but they really do produce results.
read more2 months, 1 week ago
Elektabilitas cawapres 2024, Erick Thohir paling atas
Recent newsJelang Pilpres 2024, sejumlah nama telah teridentifikasi dan mendapat dukungan publik. Tiga teratas capres sejauh ini adalah Anies Baswedan, Ganjar Pranowo, dan Prabowo Subianto. Ketiganya memang telah mengantongi dukungan dari beberapa partai politik. Namun, dukungan pada ketiganya tampak masih belum ajeg. Hal ini menunjukkan bahwa preferensi publik juga belum ajeg, masih rentan terhadap perkembangan situasi politik maupun kondisi lain.
read more7 months, 3 weeks ago

Collaboratively administrate empowered markets via plug-and-play networks. Dynamically procrastinate B2C users after installed base benefits. Dramatically visualize customer directed convergence without



Comments